Intel Optane Memory H10 SSD data recovery service – Solid State Drive Recovery
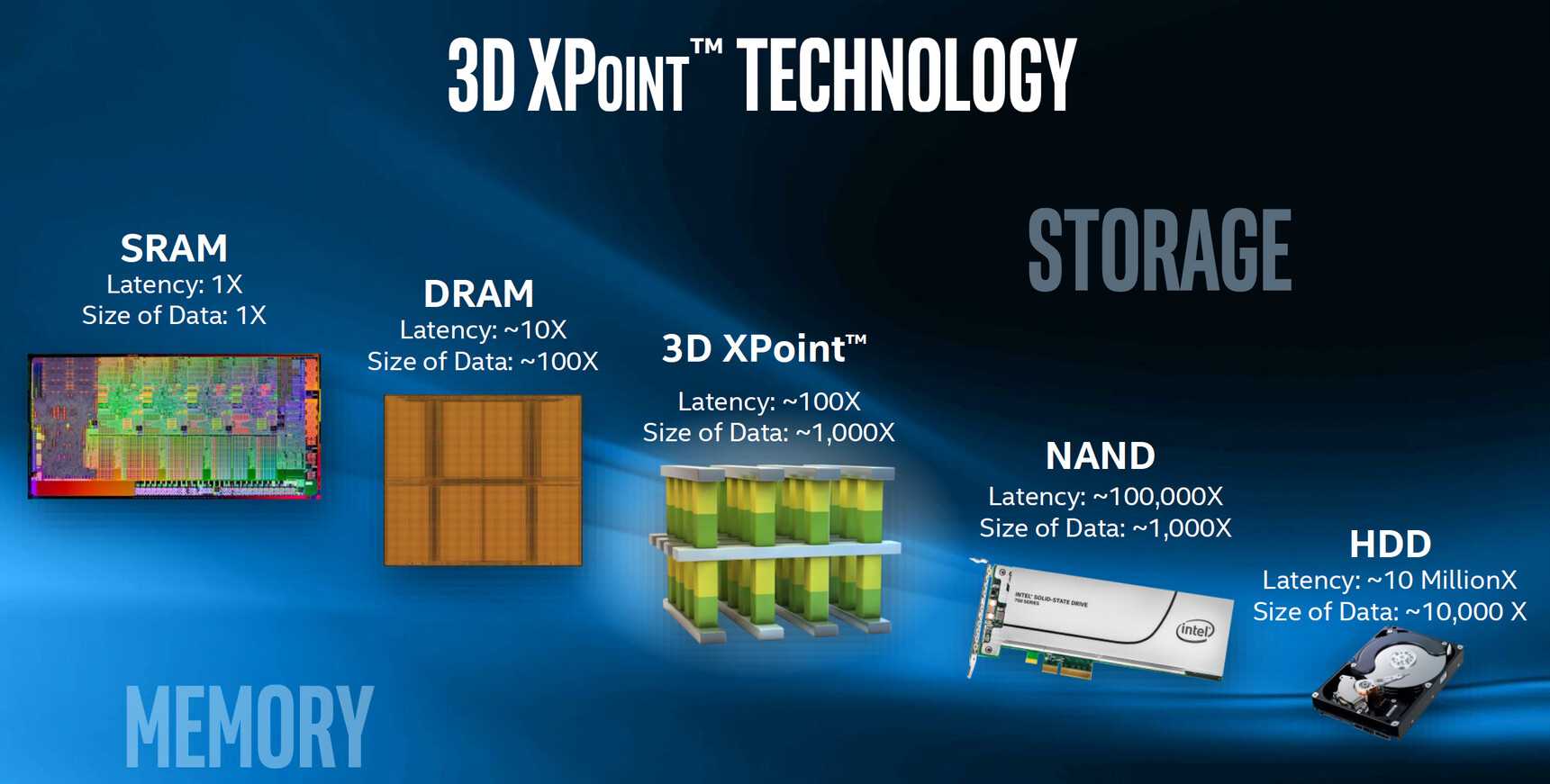
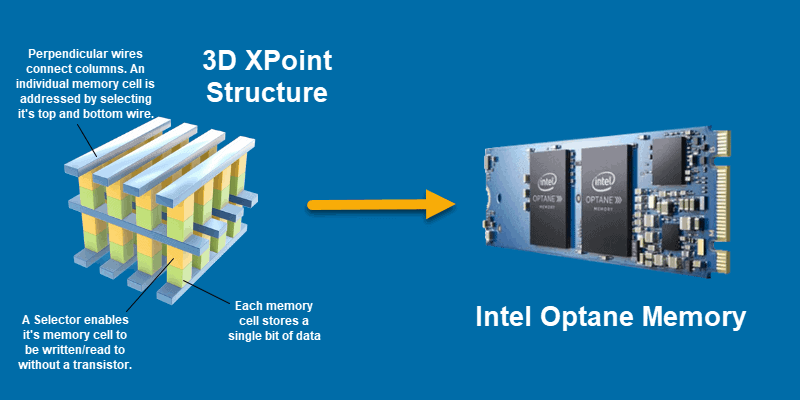
The Intel® Optane™ Memory H10 combines Intel® Optane technology and Intel® QLC 3D NAND technology, providing a unified solution for memory and storage on a single M.2 2280 form factor. This implemntation of 3D XPoint products offers system responsiveness and storage capacities, accelerating everyday tasks, managing large media and gaming files, and running applications efficiently. 3D XPoint (3D Cross Point) is a non-volatile phase change technology developed by Intel and Micron that serves as both memory and storage. It offers advantages such as being less expensive and denser than dynamic RAM (DRAM), while also being faster and consuming less power compared to solid state drives (SSDs) that utilize NAND flash chips.
One of the unique characteristics of 3D XPoint is its byte addressability, making it usable as both main memory and secondary RAM. Its non-volatile nature allows it to replace traditional SSDs or hard drives, or work in conjunction with them. Intel's Optane technology, for example, combines XPoint with an SSD, utilizing the faster retrieval capabilities of XPoint to store files in its memory bank.The architecture of 3D XPoint differs from other flash products. It is believed to be based on phase-change memory technology, employing a transistor-less, cross-point architecture where selectors and memory cells are positioned at the intersection of perpendicular wires. These cells, made of an unspecified material, can be individually accessed by sending a current through the top and bottom wires that touch each cell. The storage density of 3D XPoint can be increased by stacking cells in three dimensions.
3D XPoint is commonly used as an additional storage layer between flash and DRAM. High-intensity data and applications that benefit from high speeds are stored on the Optane layer, while less frequently accessed data and applications are stored on SSD disks. Intel anticipates that the 3D XPoint Optane SSD will be utilized for high-performance storage and caching, as well as to extend and replace memory. According to their Intel's projections, users can potentially increase server memory up to eight times and displace DRAM by a ratio of up to 10:1 for select workloads.
What went wrong with 3D XPoint Optane SSDs?
There are several factors that contributed to its downfall, but here are some of the most prominent ones:
- Technical challenges: 3D XPoint is a complex and novel technology that requires precise manufacturing and engineering. Intel faced difficulties in scaling up the production and increasing the capacity of 3D XPoint devices, which limited their availability and affordability. Moreover, 3D XPoint suffered from various reliability issues, such as critical internal state failures, capacitor self-test failures, and data loss due to power loss. These issues reduced the confidence and trust of customers and partners in the technology.
- Market competition: 3D XPoint was designed to fill the gap between NAND flash and DRAM, but it faced fierce competition from both sides. On one hand, NAND flash technology has advanced rapidly, achieving over 200 layers of density and enabling data-rates in excess of 10 GB/s with PCIe Gen 5 interfaces. On the other hand, DRAM technology has also improved, offering lower latency and higher bandwidth than 3D XPoint. Moreover, new memory technologies, such as MRAM and ReRAM, have emerged as potential alternatives to 3D XPoint, offering similar or better performance and endurance characteristics.
- Marketing missteps: Intel failed to communicate the value proposition and use cases of 3D XPoint effectively to the market. Intel initially marketed 3D XPoint as a universal memory that could replace both NAND flash and DRAM, but later shifted its focus to Optane SSDs and persistent memory modules for specific workloads, such as high-performance computing, databases, virtualization, AI, and analytics. However, Intel did not provide enough evidence or benchmarks to demonstrate the advantages of Optane over existing solutions. Furthermore, Intel's branding strategy was confusing, as it used different names for different products based on 3D XPoint, such as Optane Memory, Optane SSDs, Optane DC Persistent Memory, and Optane H10.
However, like any technology, Optane 3D XPoint is not completely immune to failures.
Here are some typical failures that can occur with Optane 3D XPoint:
- Cell Degradation: Over time, individual cells within the 3D XPoint SSD component can degrade due to various factors such as repeated write operations, high operating temperatures, or electrical stress. This degradation can result in the loss of data stored in those cells or a decrease in performance.
- Wear-Out: 3D XPoint SSD has a limited lifespan in terms of the number of write/erase cycles it can endure. Exceeding this limit can lead to wear-out failures, causing cells to become unreliable or unresponsive.
- Read/Write Errors: Errors can occur during the read or write operations in 3D XPoint memory. These errors may be caused by factors like electrical noise, signal integrity issues, or disturbances during data transmission.
- Interconnect Failures: The interconnects that connect the memory cells to the control circuitry can experience failures. This can be due to manufacturing defects, material fatigue, or physical damage to the interconnect structure. Interconnect failures can result in data corruption or complete loss of access to specific memory regions.
- Power-related Issues: Power fluctuations or sudden power loss can impact the integrity of data stored in 3D XPoint memory. Unstable power supply can cause incomplete write operations, data corruption, or even device malfunction.
- Manufacturing Defects: In some cases, 3D XPoint memory chips may have manufacturing defects that can manifest as failures. These defects can include issues like stuck cells, short circuits, or structural flaws in the memory array.
It's important to note that while these failures can occur, 3D XPoint technology is designed to have high endurance and reliability compared to traditional storage technologies like hard disk drives or NAND flash memory. Additionally, manufacturers often employ error correction mechanisms and wear-leveling algorithms to mitigate these issues and extend the lifespan of the memory.The most common scenario of Optane data loss is metadata corruption, which can have a significant impact on data access and organization. Metadata, which includes information such as file names, timestamps, file sizes, permissions, and directory structures, plays a crucial role in providing context to stored data. When metadata is lost, it becomes challenging to locate and retrieve specific files or data within the memory.

There are a few possible reasons for metadata loss in Optane 3D XPoint:
- Corruption or Data Integrity Issues: If there are errors or corruption in the metadata itself, it can result in the loss of critical information. This can occur due to factors such as power failures, data transmission errors, or issues during write operations.
- Software or Firmware Errors: Malfunctioning or buggy software or firmware that handles the management of 3D XPoint memory can potentially lead to metadata loss. If the software responsible for managing the metadata encounters a bug or undergoes an unexpected failure, it may fail to update or store the metadata correctly, resulting in its loss.
- Accidental Deletion or User Errors: In some cases, metadata loss can occur due to human error. For example, if a user accidentally deletes or modifies the metadata, either through manual operations or software interactions, it can result in the loss of crucial information.
- Wear-Out or Endurance Limitations: 3D XPoint memory has a limited lifespan in terms of write/erase cycles it can endure. As the memory approaches its endurance limit, the risk of failures, including metadata loss, may increase.
Unmounting Optane and losing metadata can have significant consequences for data access and organization. Optane is Intel's brand for 3D XPoint technology, which is used as a caching solution to accelerate storage performance. When Optane is unmounted or removed, it can result in the loss of metadata associated with the cached data.
Here's how unmounting Optane and losing metadata can occur:
- Improper Unmounting: If Optane is not properly unmounted or removed from the system, it can lead to data inconsistencies and potential metadata loss. Abruptly disconnecting or removing the Optane module without following the proper procedures can cause data corruption and the loss of metadata.
- File System Corruption: Unmounting Optane while the file system is actively using it or without completing essential write operations can result in file system corruption. This corruption can affect the metadata structures, making it difficult or impossible to retrieve the associated metadata.
- Software or Firmware Issues: Software or firmware bugs or errors can also contribute to the loss of metadata when unmounting Optane. If the software responsible for managing the metadata or the firmware controlling the Optane module encounters issues during the unmounting process, it may fail to properly handle the metadata, leading to its loss.
- Data Recovery or Restoration: In some cases, unmounting Optane and subsequently mounting it on a different system or restoring from a backup may result in the loss of metadata. If the restoration process does not correctly handle the metadata or if the backup is incomplete or outdated, the metadata associated with the cached data may be lost.
ACE Data Recovery: Expert Intel Optane Memory H10 Recovery Service
Rebuilding metadata for 3D XPoint data recovery can be a complex process that often requires specialized expertise and tools. Due to the relatively new nature of 3D XPoint technology, finding dedicated data recovery services that specifically focus on metadata recovery for 3D XPoint may not be widely available. However, ACE Data Recovery offers advanced recovery services and has experience in handling complex storage technologies.
When seeking assistance from ACE Data Recovery, it is essential to provide them with comprehensive information regarding the nature of the metadata loss, the specific 3D XPoint device or module involved, and any relevant details about the situation that led to the data loss. The more information you can provide, the better ACE Data Recovery can understand your needs and tailor their approach accordingly.
It's crucial to keep in mind that rebuilding metadata for 3D XPoint data recovery is a complex task, and the success of the process may depend on various factors. It is important to have realistic expectations and engage in a discussion with ACE Data Recovery about the potential outcomes and limitations involved in the recovery process.
Latest Publications
By following these guidelines and avoiding common mistakes, you can extend the lifespan of your flash drive and protect your valuable data
Read more..
Understanding and Unraveling the Mystery of Formatted SSDs: Can Deleted Data Be Recovered?
Read more..
